产品: BF33 Microfluidic Glass Chip for Biological Rapid Testing
Featured products
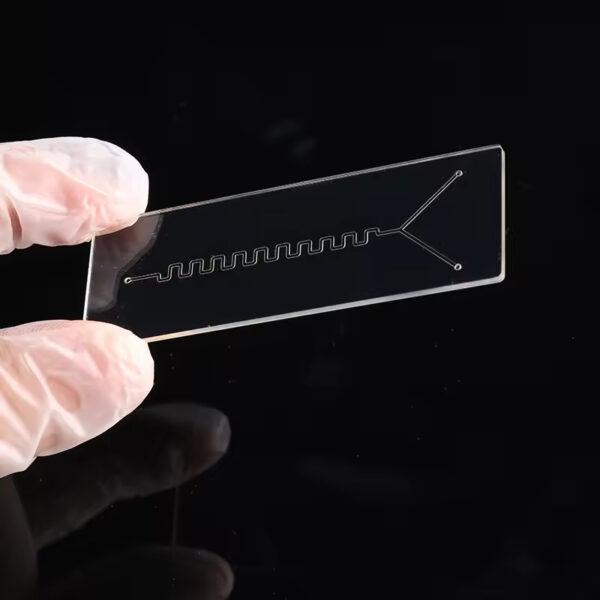
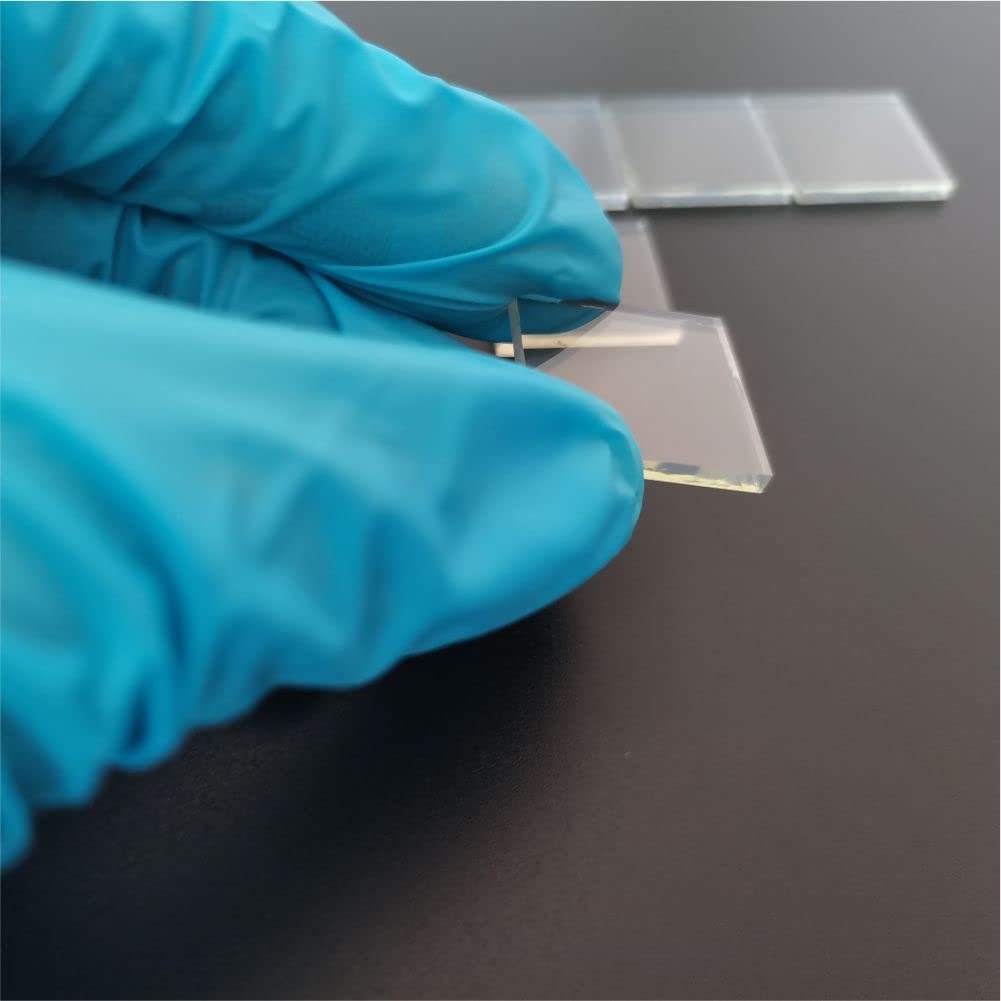
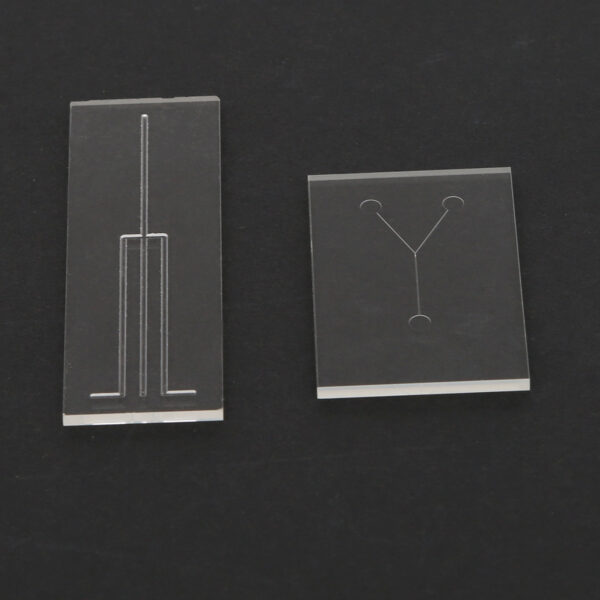
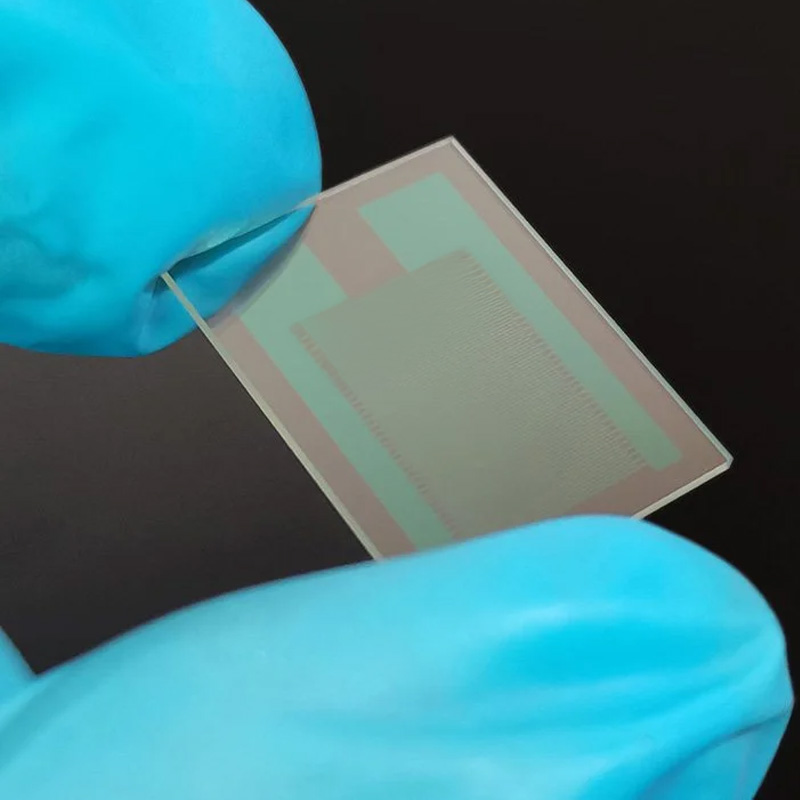
BF33 Microfluidic Glass Chip for Biological Rapid Testing
Specifications – BF33 Microfluidic Glass Chip
Material: SCHOTT BOROFLOAT® 33 Glass
Channel Width/Depth: 10–500 µm (customizable)
Thickness: 0.5 mm / 1.1 mm / 2 mm / Custom
Surface Quality: 60/40 or better
Bonding Method: Thermal bonding, plasma bonding
Application Fields: Biology, chemistry, diagnostics
What is a Microfluidic Glass Chip?
A microfluidic glass chip is a precisely etched glass substrate designed to manipulate tiny volumes of fluid—often in nanoliter or picoliter scales—through microscale channels.
This lab-on-a-chip platform integrates sample handling, mixing, reaction, and analysis into a compact device, enabling fast, cost-effective, and highly reproducible biological testing.
we manufacture microfluidic chips using BF33 glass—known for its excellent thermal stability, optical clarity, and chemical resistance.
What is a Microfluidic Chip Used For?
Microfluidic glass chips are widely used in biological and chemical testing, particularly in:
- Rapid diagnostic tests (e.g. COVID-19, pregnancy, or pathogen detection)
- DNA sequencing and PCR
- Protein analysis and immunoassays
- Cell sorting and counting
- Drug development and point-of-care testing
The design enables low reagent consumption, high throughput, and integration with optical or electrochemical sensors.
Why Choose BF33 Glass Microfluidic Chips?
TIHOTOPTICS offers premium microfluidic chips made from SCHOTT BOROFLOAT® 33 with customizable features:
- Chemical Durability – Resistant to acids, bases, and solvents
- High Optical Transparency – Suitable for optical and fluorescence imaging
- Thermal Stability – Withstands autoclaving, PCR heating, and plasma bonding
- Precision Microchannels – Created via CNC or wet etching
- Custom Designs Available – We support OEM layouts and multilayer integration
Our chips are produced in ISO-certified cleanroom facilities to ensure biological compatibility.
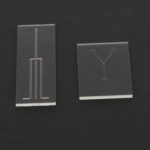
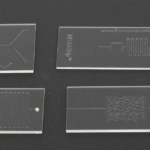
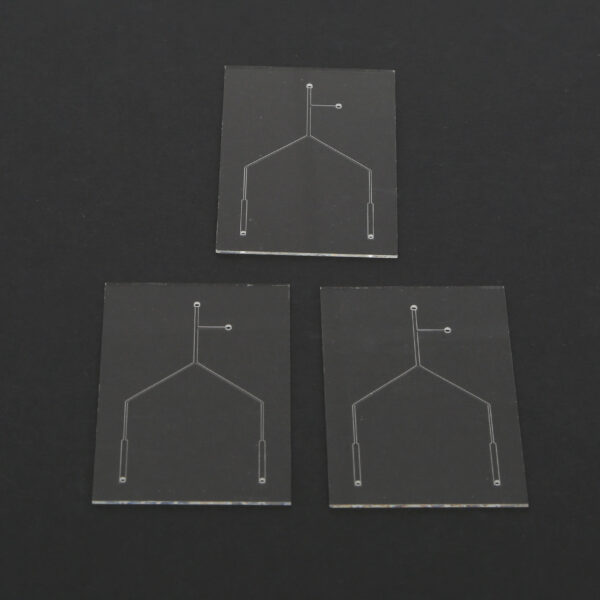
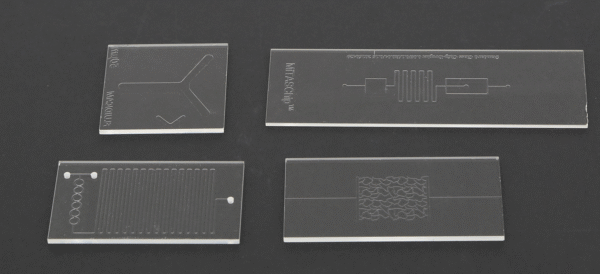
Examples of Custom Chips
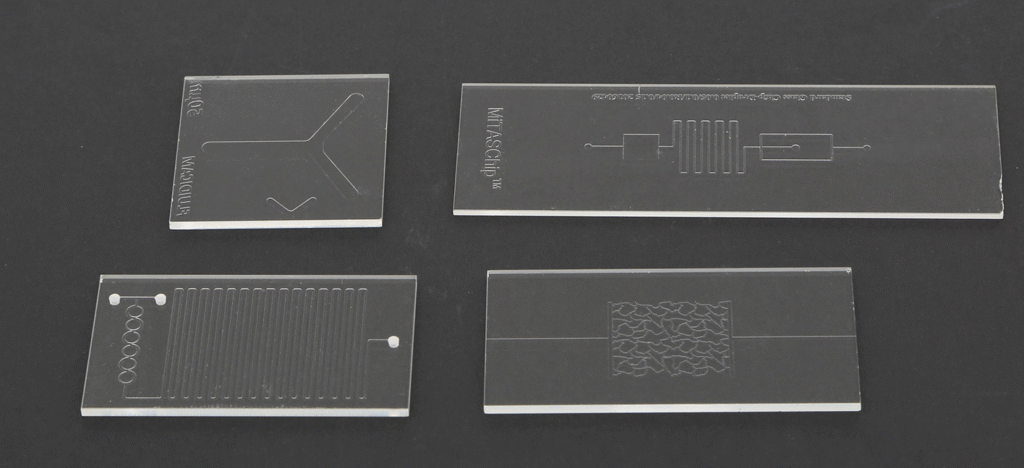
- Serpentine mixing channels for reagent analysis
- Y-shaped bifurcation channels for fluid control
- Multi-inlet reaction chambers for enzyme assays
- Spiral microchannels for particle separation
People Also Ask
What is a microfluidic glass chip used for?
Microfluidic glass chips are used to control and analyze very small volumes of fluid. They are widely applied in biological testing, DNA amplification (PCR), point-of-care diagnostics, and chemical assays.
Why use BF 33 glass for microfluidic chips?
BF33 offers excellent thermal resistance, optical transparency, and chemical durability—making it ideal for precision applications like high-temperature bonding, fluorescence imaging, and reagent compatibility.
How are microchannels made in glass chips?
Channels are typically created through CNC micromachining, wet chemical etching, or laser ablation. The chip is then sealed via thermal bonding or plasma bonding.
Can microfluidic chips be reused?
In research settings, glass chips can be reused if properly cleaned and sterilized. However, for clinical or diagnostic use, they are usually designed as single-use consumables to prevent contamination.
What’s the difference between glass and PDMS microfluidic chips?
Glass chips are more durable, chemically resistant, and optically stable—suitable for long-term and high-precision applications. PDMS (a soft polymer) is easier to prototype but less stable over time.
Do you offer custom microfluidic chip designs?
Yes. At TIHOTOPTICS, we provide full customization including layout design, channel depth, port holes, and multilayer glass chips tailored to your testing needs.
Leave Your Message